Design Thinking Prototype: 4 | Mindful Marks
Reference: Mindful Marks. (2018, June 09). 4. Design Thinking: Prototype [Video]. YouTube.
We Make Your Education Count

Get the Credit You Deserve and Become the Most Attractive Job Candidate by Earning and Posting A+ Badges to Your Linkedin Profile.
Sign Up to Get Started at Accredicity
|
Unlock the secrets of designing the perfect prototype with this insightful video. Pattie Belle Hastings explains the fourth step in the Design Thinking Prototype. This involves creating a mock-up of whatever is being designed to explore how it is working or not working, inspire users, and collect data. Prototypes can take various forms such as cardboard mock-ups, wireframes, paper prototypes, book dummies, and more. The process also involves failure, iteration, and revisiting empathy, define, and ideate phases if needed. Ultimately, prototypes are a chance to have a conversation about the design and if it is meeting the needs and creating the desired feeling in users. Learning Outline1. Prototyping is a way to explore whether the problem identified is the right one and to make sure the design meets the needs and creates the desired feelings for the users. Instructional ContentDesign Thinking is a powerful process for problem solving and innovation. In the fourth stage of Design Thinking, the Prototype stage, a physical mock-up is created to explore how a potential solution to a problem will work or not. This mock-up helps inspire users, clients, and colleagues to collect data on what is working and what is not. It is important to remember that failure is inevitable but necessary to create the best product. Iteration is also key in this stage, creating multiple versions and variations of the prototype. Lastly, what is learned from the prototype may mean revisiting previous stages of the design process. Prototypes can take various forms, depending on the product or service being designed. This could be a cardboard mock-up, wireframe, low fidelity mock-up, paper prototype, book dummy, animatic, or maquette. Walkthroughs or tests may also be conducted to determine if a process works as expected. Design Thinking is an invaluable process for problem solving and innovation. Throughout the Prototype stage, designers create physical mock-ups to explore and inspire users, collect data, and determine if a potential solution is the right one. Prototypes can be created in various forms and tests may also be conducted to ensure that processes work as expected. This stage is essential for creating the best product or service possible. Leadership
|
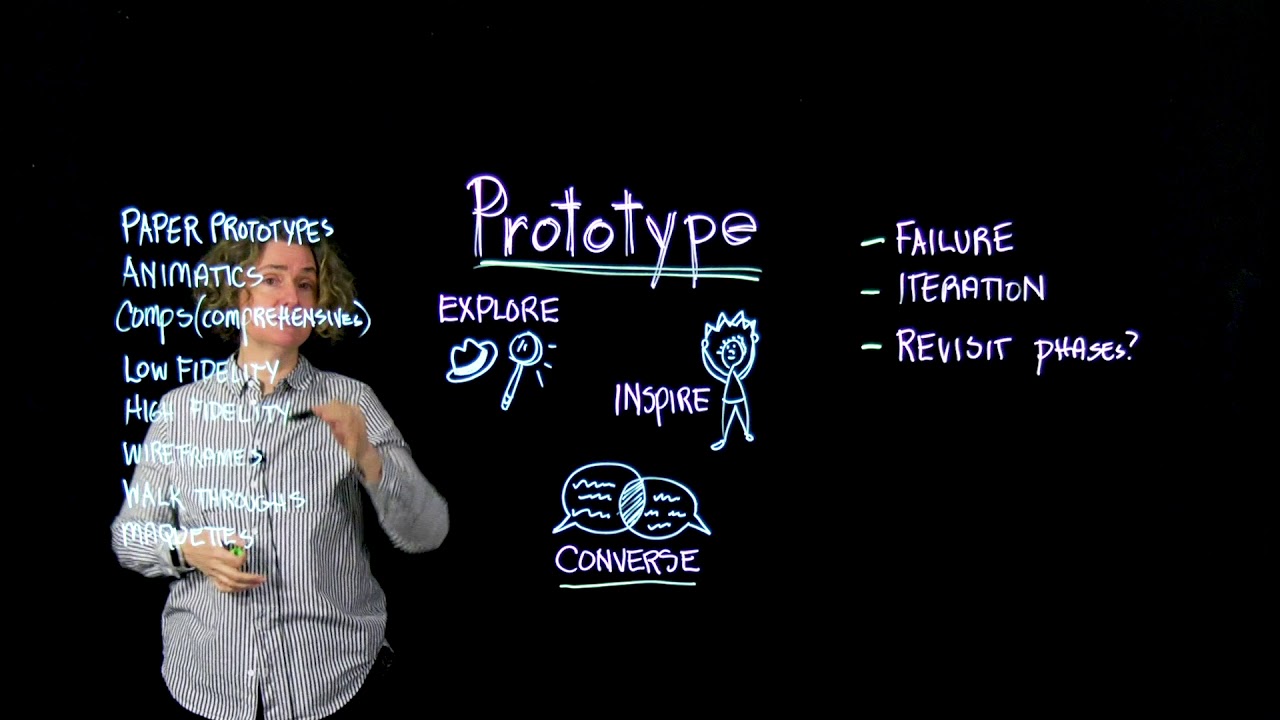
Prototyping is like making a model of a building before you build it. It's a way to check if the problem you are trying to solve is the right one. You can make a physical mock-up, a wireframe, a low-fidelity mock-up, or a paper prototype, and explore how it's working. It's important to embrace failure and make many versions, like building a tower out of Legos and then taking it apart and trying again. Prototypes help us inspire our users, and learn what works and what doesn't! Video Quotes"We want to explore how this thing is working or not working we want to inspire our users or our colleagues and collaborators by putting something in their hands" - Pattie Belle Hastings "The more we can release and let go and move on to a new idea or a new design the faster the better the product will be in the end" - Pattie Belle Hastings "We might start out with low fidelity paper prototypes test those with users and then take them to higher fidelity until they're actual high functioning high fidelity prototypes" - Pattie Belle Hastings Related Quotes1. “If you don't have the ability to see something from the perspective of the user, you’re not going to be able to design something that actually serves them.” -Joe Toscano, User Experience Designer 2. “It’s really important to understand that prototyping is not just about the physical, tangible objects. It’s also about the experiences.” -Nilofer Merchant, Author 3. “Prototyping is a way of learning. It’s a way of finding out what works and what doesn’t.” -Christina Wodtke, Design Thinking Expert Competencies1. Creativity and Innovation Learning Outcomes1. Understand the importance of prototyping in the design thinking process (Knowledge) Sample Answers1. Prototyping is an important step in the design thinking process. It involves creating a mock-up of a product or service to explore if it meets the needs of the users. It can be a physical prototype, wireframe, low fidelity mock-up, paper prototype, or something else. 2. Prototyping helps to inspire users and colleagues, and collect data on what works and what doesn't. Iteration is also important, as it involves multiple attempts to get the best results. 3. Prototypes can take different forms, such as cardboard mock-ups, wireframes, comps, low fidelity, and high fidelity prototypes. Maquettes and walkthroughs are also useful when designing services, and point-of-purchase designs. Pattie Belle HastingsPattie Belle Hastings is an American-based Design Thinking & UX/UI Design specialist and educator. She has over 20 years of experience in the design industry, with a passion for teaching and helping people unlock their creative potential. She has a Masters in Design from the Academy of Art University, and an undergraduate degree in Graphic Design from San Jose State University. She is an expert in Design Thinking and Prototype because she has a deep understanding of the process and how to effectively apply it to real-world design challenges. Pattie Belle Hastings is the founder of Mindful Marks, a company dedicated to helping people become more mindful, empathetic, and creative in their design process. She also serves as an adjunct professor at Stanford University and the Rhode Island School of Design. Pattie Belle Hastings Learning DesignThe three competencies of creativity and innovation, problem solving, and decision making are essential for effective leadership. These competencies are important for leaders to have in order to effectively lead teams, to develop innovative solutions, and to make sound decisions that benefit the organization. In order to help students build these competencies, a framework such as the 4C/ID model can be used. This model focuses on four different areas of leadership competencies: communication, collaboration, critical thinking, and creativity/innovation. This model can be used to help students identify and develop their own competencies in these areas. A pedagogical approach such as experiential learning can also be used to help students build these competencies. Experiential learning is an approach that focuses on learning through experience. AssessmentQ: What is the purpose of prototyping? A. To inspire people to find out and collect more data about what is working and what is not working QuestionsCommon Questions: Real-Life Application Questions: KeywordsDesign Thinking, Prototype, Low Fidelity, High Fidelity, Point-of-Purchase, Motion Graphics, Public Service, Paper Prototype, Mobile Application, Wireframe Walkthrough Facts1. Design Thinking Process includes Empathy, Ideate, Prototype, Test and Implement. Trends1. Design a series of prototypes for a mobile application, including a low-fidelity and high-fidelity version, to test the user experience from start to finish. 2. Create a comprehensive branding package that includes a paper prototype that effectively communicates the desired message. 3. Design a service walkthrough to explore how to redesign a customer service process, such as the TSA, to make it more efficient. 4. Create a point-of-purchase maquette to test different design variants for physical stores. 5. Develop an animatic to test the story and movement for an animation or public service announcement. SourceThis learning instructional guidance was formulated using the GPT-3 language model created by OpenAI. ShareExplore & prototype your ideas to craft the perfect product/service for your users. #DesignThinking #Prototyping #Iteration #LowFidelity #HighFidelity 🙂 @Accredicity |








 5 Creds - Leadership
5 Creds - Leadership



